- School District of Beloit
- 6th Grade - Math
6th Grade - Math
-
The School District of Beloit selected a high-quality math curriculum aligned to WI state standards that incorporates research-based instructional strategies to support all students in their mathematical learning. The goal of the math program is to prepare our students for their future, which could be very different from the world we live in today. As a result, we make an effort to establish a solid foundation in problem solving, conceptual comprehension, procedural fluency, and applying math to real-world situations. At all grade-levels, lessons build on a student’s prior math knowledge to help prepare them for future math learning.
6th Grade Units
-
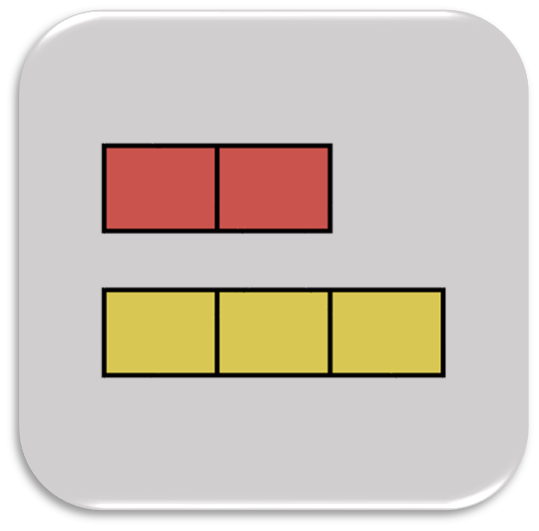
Ratios, Rates, and Percents
Students are introduced to ratio reasoning. They use tape diagrams, double number lines, tables, and graphs to model and compare ratio relationships, determine equivalent ratios, and solve real-world problems. Then, students develop an understanding of rates associated with ratio relationships. They calculate unit rates and use them to solve problems involving speed, unit pricing, measurement conversions, and other real-world applications. Students understand a percent as a fraction with a denominator of 100, and they apply their ratio and rate reasoning to solve for the unknown percent, part, or whole in real-world problems.
-
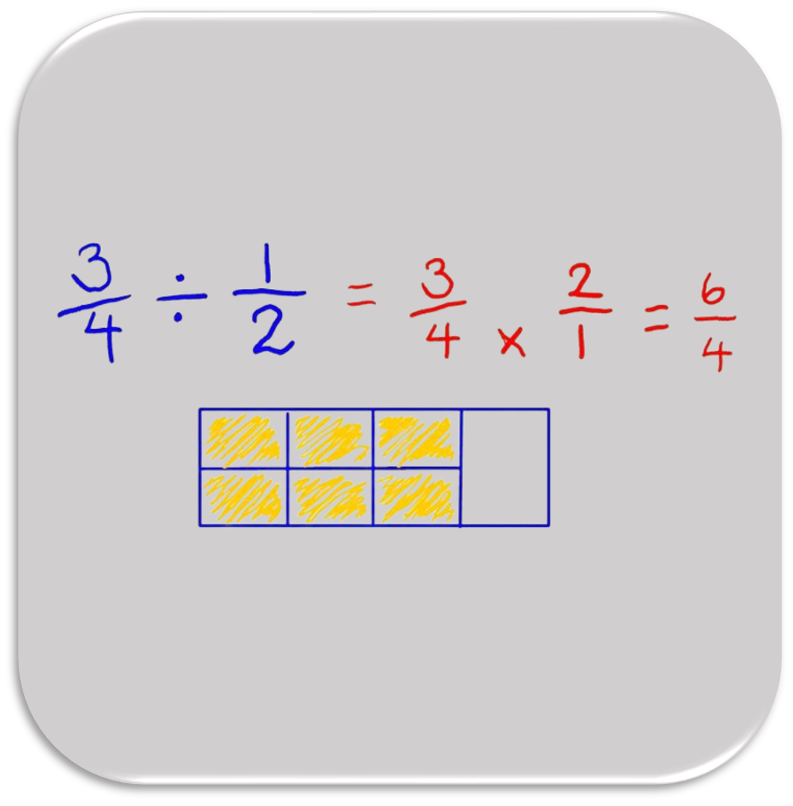
Operations with Fractions and Multi-Digit Numbers
Students begin by using visual models and an understanding of divisibility to find the greatest common factor and least common multiple of pairs of numbers. Then, students apply their previous understanding of multiplication and division to divide fractions by fractions. They model fraction division expressions with tape diagrams and double number lines, use common denominators to divide fractions by fractions, and then develop and apply the invert and multiply strategy. Students use standard algorithms to fluently add, subtract, and multiply decimals, and apply those skills in real-world applications. They extend their understanding of division from prior grades to use the standard division algorithm to divide multi-digit numbers and decimals.
-
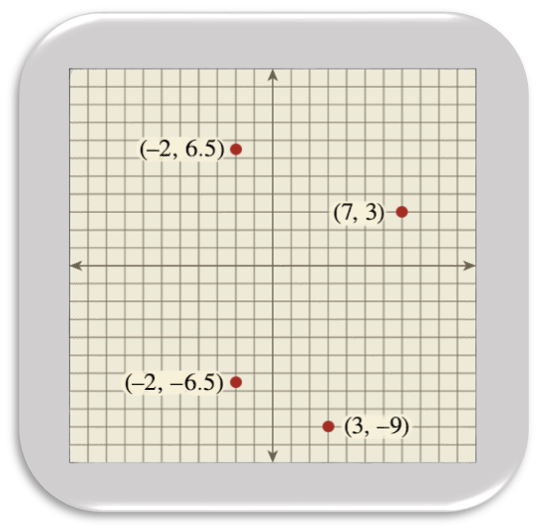
Rational Numbers
Students will develop an understanding of rational numbers and use rational numbers to describe real-world quantities. Students plot rational numbers and their opposites on a number line, calculate absolute values, order and compare rational numbers, and apply the concept of magnitude to describe and compare real-world quantities. Students explore the structure of the four quadrants of the coordinate plane. They plot and locate points with rational number coordinates, reflect points across one or both axes, calculate the lengths of lines segments, graph geometric figures, and use the coordinate plane to solve problems.
-
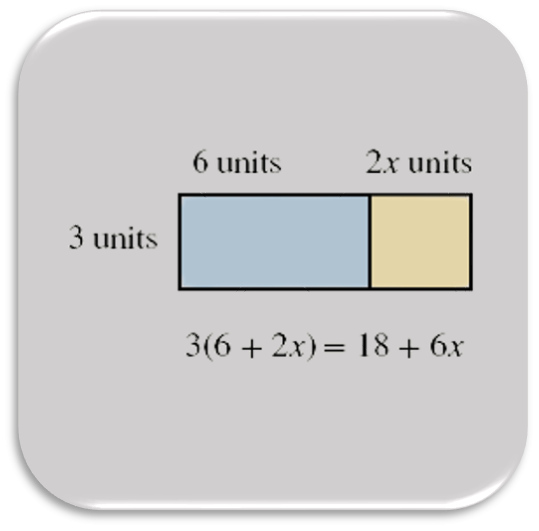
Expressions and One-Step Equations
Students work with numerical and algebraic expressions and equations. First, they learn that exponents represent repeated multiplication, evaluate powers with whole numbers, fractions, and decimal bases, and use the order of operations to evaluate numerical expressions. Then, students learn why and how to use variables to represent unknown numbers and quantities. They write and evaluate algebraic expressions and use properties of operations to generate equivalent expressions. Students reason about and solve single-variable, one-step equations, and they understand the meaning of a solution to an equation or inequality. Students revisit ratio relationships and write and graph equations in two variables, identifying independent and dependent variables in real-world situations.
-
Area, Surface Area, and Volume
Students use their understanding of the areas of rectangles to develop formulas for the area of a parallelogram and the area of a triangle. Students apply their prior knowledge of area, equivalent numerical expressions, the properties of operations, and coordinate graphing as they find the areas of composite polygons and trapezoids. They identify attributes of the faces of right prisms and pyramids and use the net of a solid to determine its surface area. By packing right rectangular prisms with cubes of fractional edge lengths, students determine that the formulas
-
Statistics
Students begin to think and reason statistically. They identify statistical questions and represent data distributions by using dot plots, histograms, relative frequency histograms, and box plots. Students describe the center, spread, and shape of a data distribution. They calculate and interpret measures of center and spread, including mean, mean absolute deviation, median, and interquartile range, and they use these measures to describe the typical value and variability of a data distribution. Students will complete a project where they develop a statistical question, implement a plan to collect data, analyze and interpret the data they collect, and present their findings to their peers.
By the end of 6th Grade, students will...
-
- use tape diagrams to model ratios and solve problems.
- explore different ways to group and compare objects to develop an understanding of equivalent ratios by the end of the topic.
- develop an understanding of the rates associated with ratio relationships.
- compare ratio relationships in context by using ratios to answer real-world questions.
- represent ratio relationships by using ratio tables, double number lines, and points in the coordinate plane.
- calculate unit rates
- model fraction division with tape diagrams and number lines, reason about the relationship between multiplication and division, and interpret fraction division problems as number of groups unknown or group size unknown.
- use number sense and place value reasoning to add and subtract decimals and determine the placement of the decimal point in sums and differences.
- learn to express quotients as decimals and round quotients when needed.
- fluently add, subtract, and multiply multi-digit decimals.
- apply their understanding of decimal division to solve multi-step real-world problems.
- plot whole numbers and opposites of whole numbers on horizontal and vertical number lines and discover that these numbers are called integers.
- calculate the lengths of horizontal and vertical line segments in the coordinate plane, both by counting units and by applying their understanding of absolute value.
- encounter real-world problems related to the coordinate plane, such as street maps on a grid and the geographic coordinate system.
- transition from numerical expressions to algebraic expressions and learn why and how to use variables to represent unknown numbers and quantities.
- interpret the meanings of points on graphs and also interpret the meanings of coefficients, variables, operators, and constants in equations that represent real-world situations.
- write, interpret, and evaluate numerical expressions.
- use the distributive property to write products as sums or differences, to factor algebraic expressions, and to combine like terms.
- extend their understanding of areas of polygons to develop the formulas for the area of a parallelogram and the area of a triangle.
- solve problems involving figures graphed in the coordinate plane, using their understanding of rational number coordinates to determine side lengths and find the perimeters and areas of figures.
- solve real-world and mathematical problems by finding the areas of triangles.
- visualize and represent data distributions by using dot plots, histograms, and relative frequency histograms.
- develop a statistical question and then create and use a plan to collect data.
- analyze data by creating data displays and calculating numerical summaries.
- interpret their results to answer a statistical question and present their findings to their peers.



