- School District of Beloit
- 3rd Grade - Math
3rd Grade - Math
-
The School District of Beloit selected a high-quality math curriculum aligned to WI state standards that incorporates research-based instructional strategies to support all students in their mathematical learning. The goal of the math program is to prepare our students for their future, which could be very different from the world we live in today. As a result, we make an effort to establish a solid foundation in problem solving, conceptual comprehension, procedural fluency, and applying math to real-world situations. At all grade-levels, lessons build on a student’s prior math knowledge to help prepare them for future math learning.
3rd Grade Math Units
-
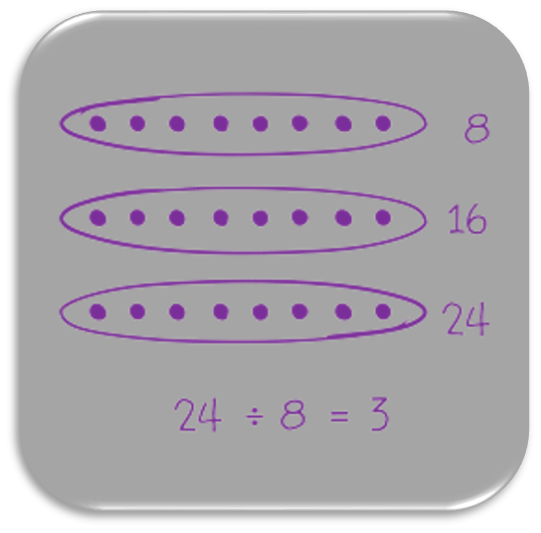
Unit 1 - Multiplication and Division with Units of 2,3,4,5, and 10
Students relate repeated addition, equal groups, and arrays to multiplication and division. With a focus on units of 2, 3, 4, 5, and 10, students use the commutative and distributive properties as strategies to multiply, and they write expressions with three factors as a foundation of the associative property. Students express division as both unknown factor problems and division equations and break apart and distribute the total to divide. They use their understanding of multiplication and division concepts to reason about and solve one- and two-step word problems.
-
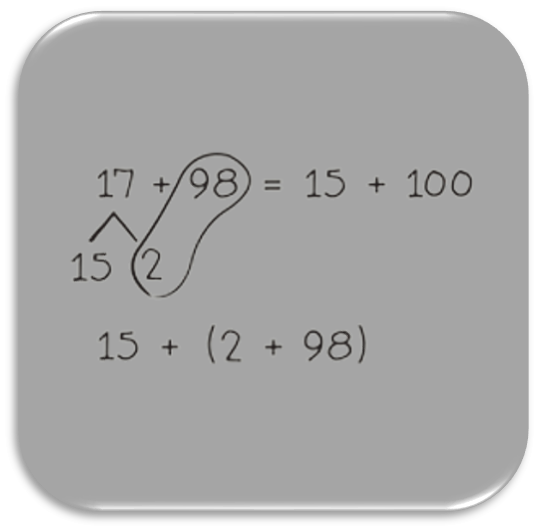
Unit 2 - Place Value Concepts through Metric Measurement
Students compose and decompose metric measurement units and relate them to place value units up to 1 thousand . They use place value understanding and the vertical number line to round two- and three-digit numbers. Students also add and subtract two- and three-digit numbers within 1,000 by using a variety of strategies, including the standard algorithm.
-
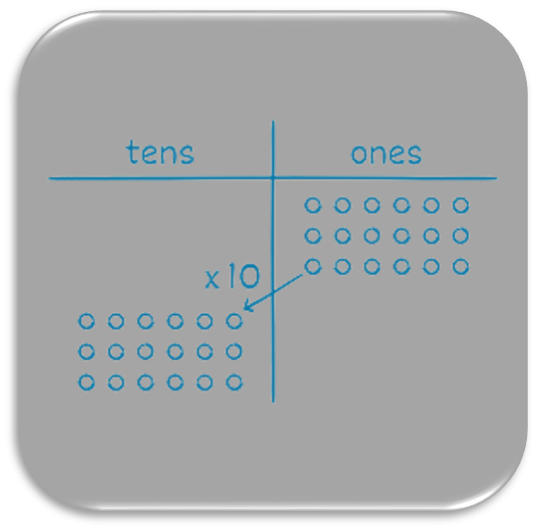
Unit 3 - Multiplication and Division with Units of 0,1,6,7,8, and 9
Students extend their learning of multiplication and division to units of 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, and 1 by applying conceptual understanding and by using the commutative, distributive, and associative properties, as applicable. They multiply with two-digit multiples of 10 and solve one- and two-step word problems involving the four operations.
-
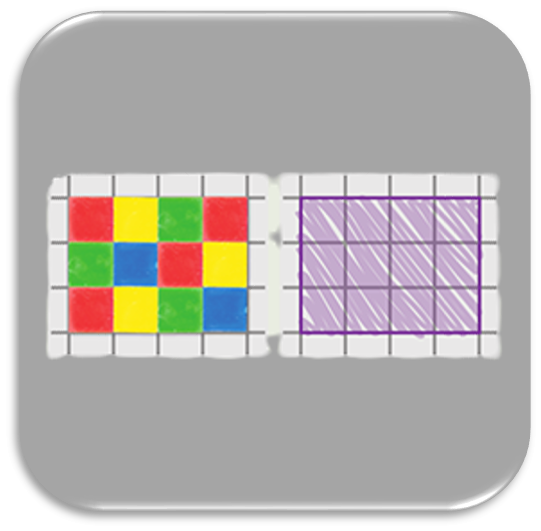
Unit 4 - Multiplication and Area
Students recognize area as an attribute of two-dimensional regions. They measure the area of a shape by finding the total number of same-sized square units required to cover the shape without gaps or overlaps. Students understand that rectangular arrays can be decomposed into identical rows or identical columns. They connect the number of rows and columns to the side lengths and then connect area to multiplication. Students use multiplication to determine the area of a rectangle and apply area concepts and strategies to mathematical and real-world problems.
-
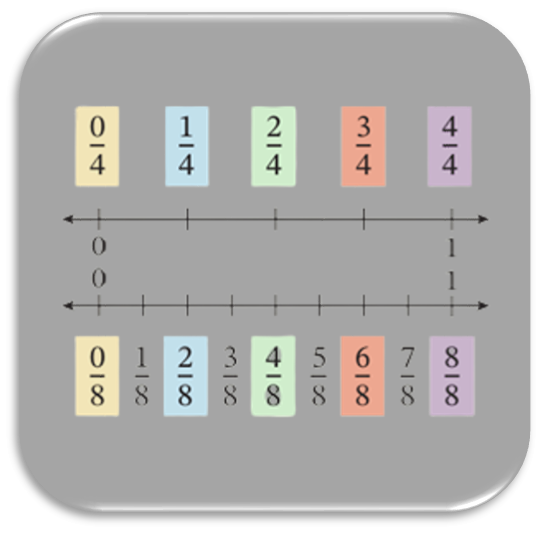
Unit 5 - Fraction as Numbers
Students develop an understanding of fractions as numbers. They partition a whole into equal parts and recognize 1 of a fractional unit as a unit fraction. Students compose non-unit fractions from unit fractions and use visual fraction models and written fractions to represent parts of a whole. Students use fractions to represent numbers equal to, less than, and greater than 1. They compare fractions by using visual fraction models and by reasoning about the size of fractions that have the same numerator or denominator. Students identify equivalent fractions, and they apply fraction concepts by using rulers to measure to the nearest quarter inch and by plotting fractional length data on line plots.
-
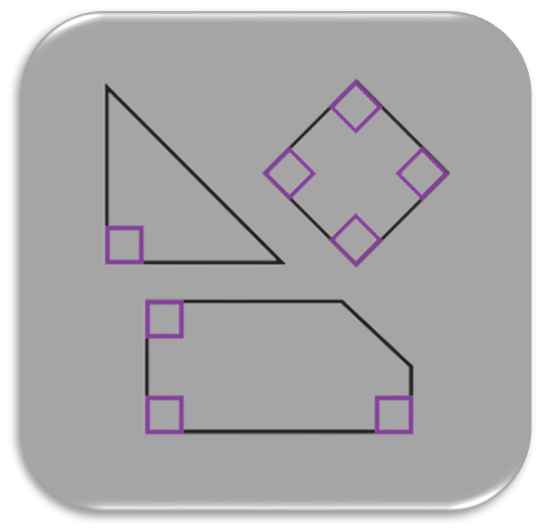
Unit 6 - Geometry, Measurement, and Data
Students tell time to the nearest minute and use linear models to solve and represent elapsed time word problems. Students describe, analyze, and compare properties of two-dimensional shapes. They compare and classify shapes by the number of sides and angles and make connections to the attributes of shapes. Students recognize perimeter as an attribute of plane figures and solve real-world and mathematical problems involving perimeter. Students also represent and interpret data by using scaled picture graphs, scaled bar graphs, and line plots.
By the end of 3rd Grade, students will...
-
- represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division.
- understand properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division.
- multiply and divide within 100.
- solve problems involving the four operations, and identify and explain patterns in arithmetic.
- use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic.
- develop an understanding of fractions as numbers.
- solve problems involving measurement and estimation of intervals of time, liquid volumes, and masses of objects.
- understand concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and to addition.
- recognize perimeter as an attribute of plane figures and distinguish between linear and area measures.



